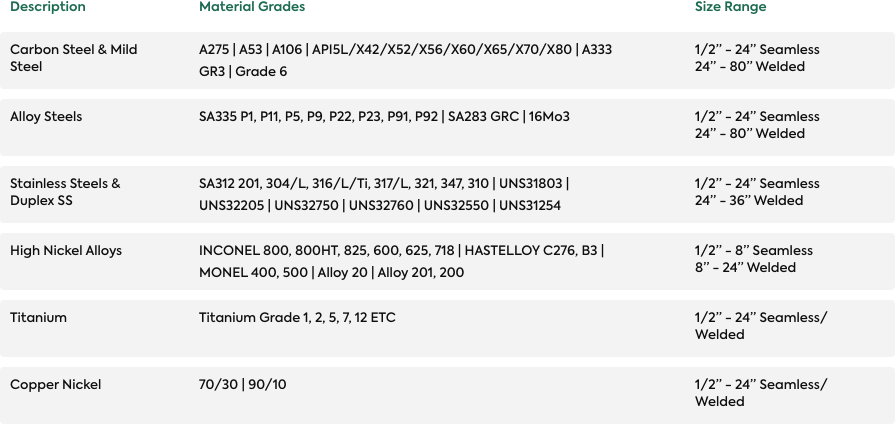
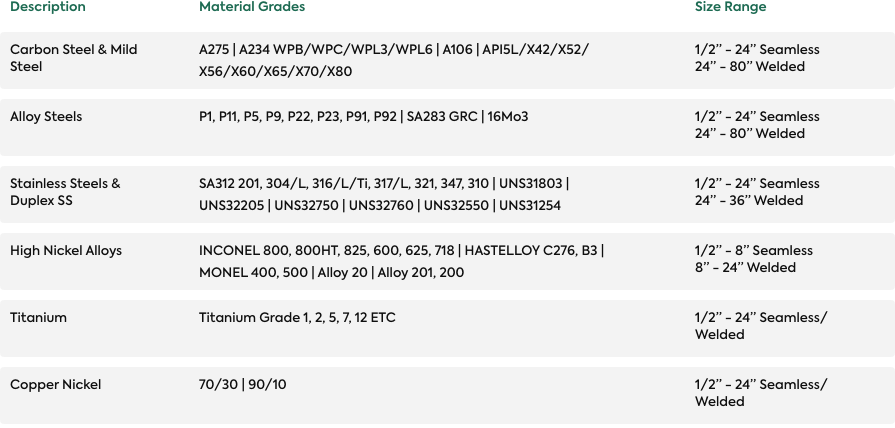
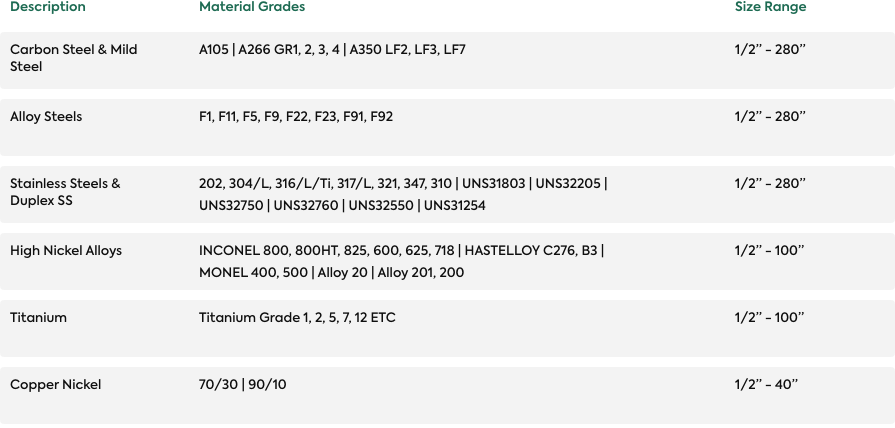
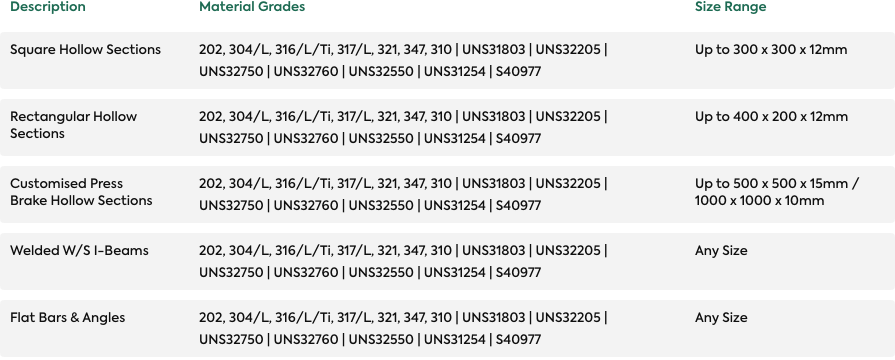
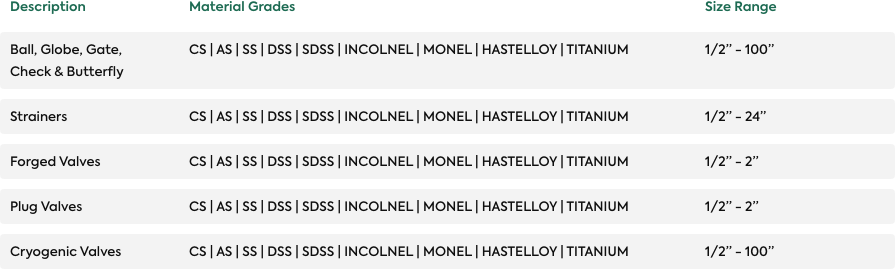
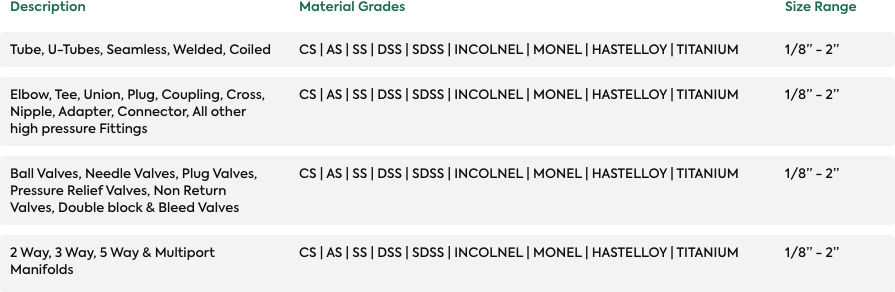
Forms






Alloy 59 Applications
Alloy 59 is suitable for a wide spectrum of applications in chemistry, petro chemistry, energy and environmental
engineering. Typical applications are:
- Plant components for organic chemistry processes with media containing chloride, especially where catalytic
systems on chloride basis are used. - Multi-purpose plants in the chemicals industry.
- Plant parts in active substance preparation and the pharmaceuticals industry.
- Scrubber, heat exchangers, flaps, ventilators and agitators for flue gas desulfurization (FGD) in fossil fuel power
plants and waste combustion plants. - SO2-washers for ship diesel engines.
- Components for seawater and concentrated brines.
- Equipment and components for geothermal energy and acid gas applications.
- Reactors for acetic acids and acetic anhydrides.
- Reactors for hydrofluoric acid.
- Sulfuric acid coolers.
Alloy 59 is a nickel-chrome-molybdenum alloy , which has particularly low concentrations
of carbon and silica and it is characterized by excellent corrosion resistance as well as high strength.
Alloy 59 is characterized by:
- Excellent resistance against a multitude of corrosive media under oxidizing and reducing conditions.
- Outstanding resistance against chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion, as well as resistance against stress
corrosion cracking. - Excellent resistance in mineral acids such as nitric, phosphoric, sulfuric and salt acids, but especially against
sulfur/salt acid mixtures. - Excellent resistance in contaminated mineral acids,excellent resistance in contaminated mineral acids.
- Very good processing characteristics and weldability with low propensity to form hot cracks.
- Very resistant to sensitivation.
Alloy 59 Plate Standards
| Bar | 17752 17744 |
- | SB 574 SB 564 |
B 574 B 564 |
| Sheet | 17750 17744 |
- | SB 575 | B 575 |
| Strip | 17744 | - | SB 575 | B 575 |
| Wire | 17744 | - | - | - |
Alloy 59 Designations
| EN | 2.4605 – NiCr23Mo16Al |
| ISO | 15156/MR 0175 |
| UNS | N06059 |
Alloy 59 Chemical Composition
| Min | - | 22.0 | Balance | 15.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.1 | - |
| Max | 1.5 | 24.0 | Balance | 16.5 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.015 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
Alloy 59 Physical Properties
| 8.6 g/cm3 (537 lb/ft3) | 1,310 - 1,360 ℃(710 - 738 ℉) | 1.001 (Maximum) |
| Specific Heat | 414/0.0989 | 434/0.104 | 443/0.106 | 451/0.108 | 459/0.11 | 464/0.111 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10.4/6.01 | 13.7/7.92 | 15.4/8.90 | 17.0/9.82 | 18.6/10.7 | 20.4/11.8 |
| Electrical Resistivity | 126 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 134 | 133 |
| Modulus Of Elasticity | 210/30.5 | 200/29.0 | 196/28.4 | 190/27.6 | 185/26.8 | 178/25.8 |
| Co-efficient of Thermal Expansion | -/- | 12.2/6.78 | 12.5/6.94 | 12.7/7.06 | 12.9/7.17 | 13.1/7.28 |
Alloy 59 Mechanical Properties
| Yield Strength MPa/ksi |
340/49.3 | 250/36.3 | 220/31.9 | 175/25.4 |
| Tensile Strength MPa/ksi |
690-900/100-131 | 615/89.2 | 580/84.1 | 525/76.1 |
| Elongation % |
40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
Alloy 625 Inventory
| Alloy 625 Pipe | 0.5 in | 8 in |
| Alloy 625 Coil | 0.25 mm | 3.18 mm |
| Alloy 625 Welding Wire | 0.5 mm | 3.175 mm |
| Alloy 625 Sheet and Plate | 0.25 mm | 76.2 mm |
| Alloy 625 Round Bar | 12 mm | 260 mm |
| Alloy 625 Pipe Fittings | 0.5 in | 8 in |
| Alloy 625 Flanges | 0.5 in | 8 in |
Welding Alloy 59
Alloy 59 can be welded using conventional processes with metals of the same type as well as many other metals.
This includes TIG, GMAW (MIG/MAG), plasma, electron beam welding and handheld electrical welding. The use of a pulse technique is preferable during shielding gas welding processes.
The use of a multi-component shielding gas (Ar + He + H2 + CO2) with low CO2 concentrations (< 0.12%) is recommended for the MAG process.
For welding,Alloy 59 should be in a solution-annealed condition and free of scale, grease and markings. When welding the root, care should
be taken to achieve best quality root protection using pure argon (argon 4.6) so that the welding edge is free of oxides
after welding the root.
Root protection is also recommended for the first and, in certain cases depending on the welded construction, also for the second intermediate layer weld after root welding. Any heat tint in the intermediate layers must
be removed while the welding edge is still hot, preferably by means of a stainless steel brush.
Filler metal
The use of the following fillers is recommended for gas-shielded welding methods:
| Welding rods and wire electrodes |
|---|
|