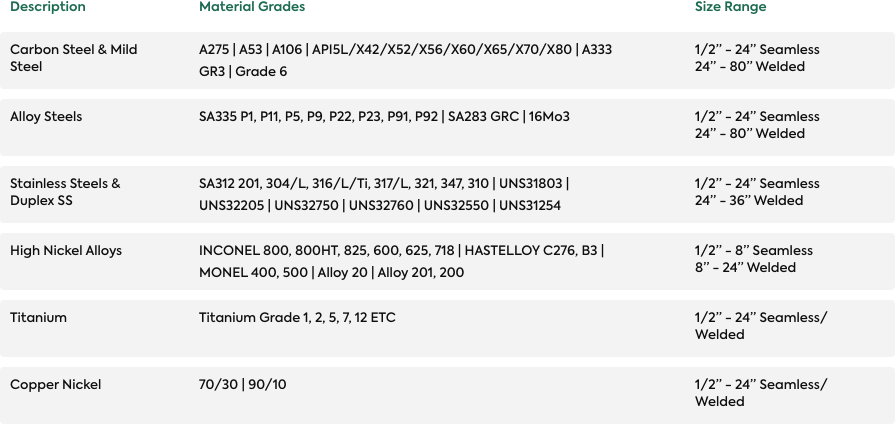
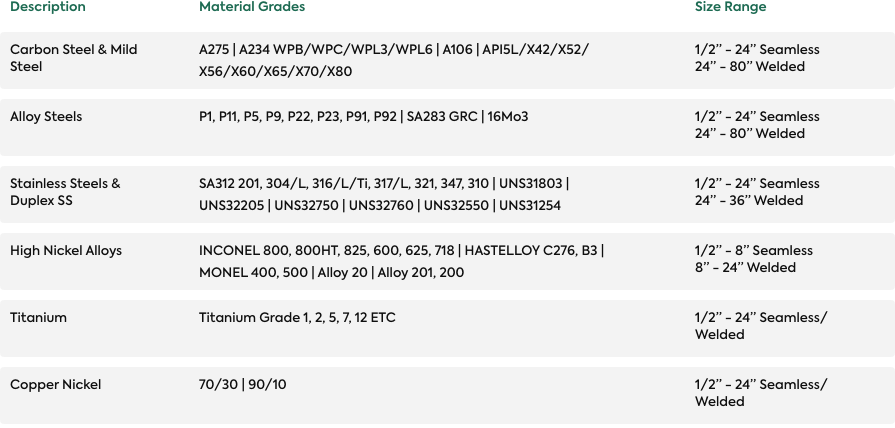
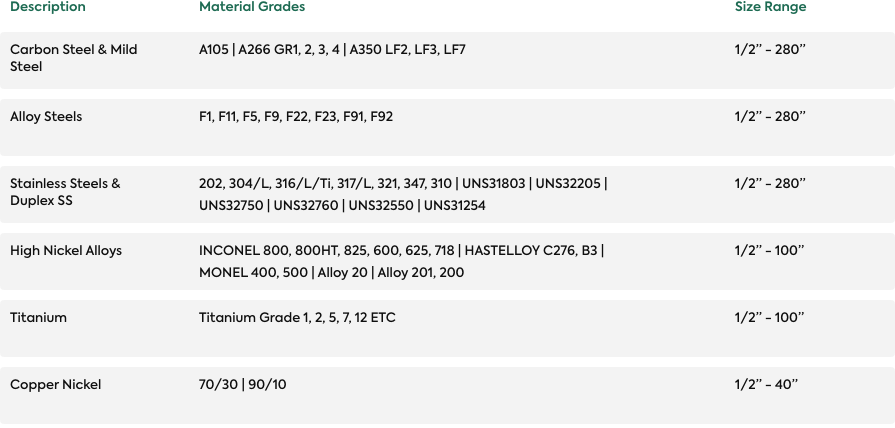
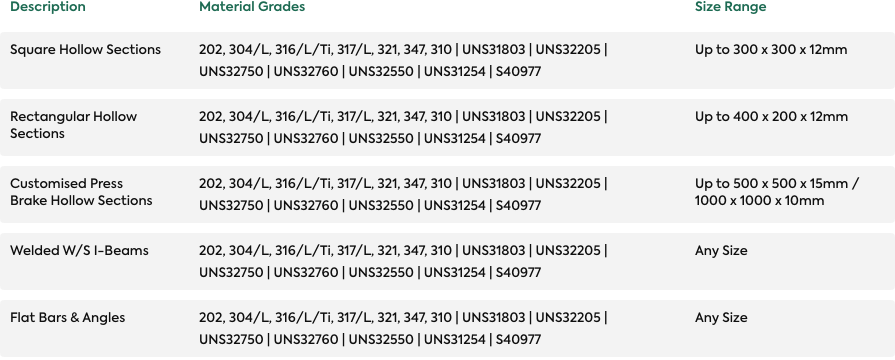
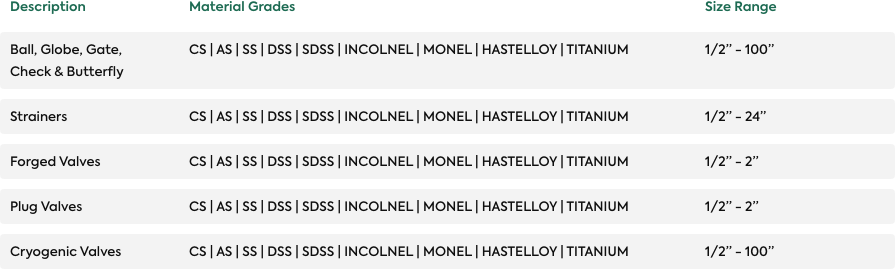
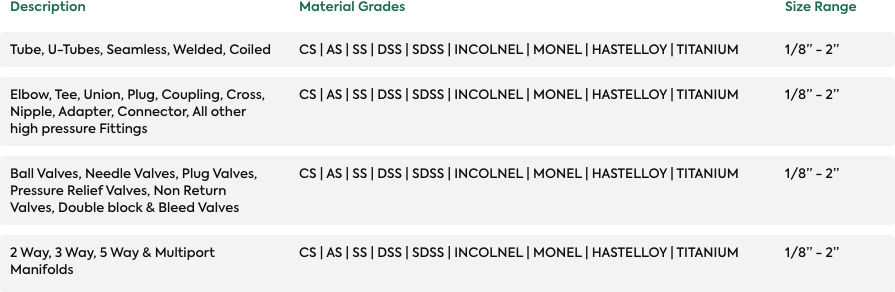
Forms






Alloy 602 Applications
Alloy 602 CA has a wide range of application in the high-temperature field of thermo-technical and chemical processes, in power plants and in the automotive industry.
Typical applications are:
- Radiant tubes.
- Furnace muffles.
- Rotary and shaft furnaces.
- Kiln rollers and other furnace installations.
- Glass pot for melting radioactive waste.
- Methanol and ammonia synthesis.
- Hydrogen production.
- Reformers in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
- Components in automotive exhaust systems.
- Glow plugs for diesel engines.
Alloy 602 CA is a high-temperature material with excellent resistance to creep and oxidation up to 1,200 °C
(2,192 °F). Alloy 602 CA is delivered in the solution-annealed state with an oxidized or descaled surface. The
material features to be emphasized are:
- Excellent high-temperature creep behaviour values.
- Outstanding resistance to oxidation at high temperatures, even under cyclical conditions.
- Very good corrosion resistance in carburizing and oxidizing/chlorinating media.
- Approval for pressure containers with operating temperatures from -10 to 1,150 °C (14 to 2,102 °F) according
to VdTÜV material data sheet 540 and up to 1,650 °F (899 °C) according to ASME Code Section I as well as
up to 1,800 °F (982 °C) for applications according to section VIII Div.I.
Alloy 602 Plate Standards
| Rod,Bar | 17742 17752 |
10302 | B 166 | SB 166 SB 166 |
| Sheet,Plate | 17742 17750 |
10302 | B 168 | SB 168 |
| Strip | 17742 17750 |
10302 | B 168 | SB 168 |
| Wire | 17742 | - | B 166 | SB 166 |
Alloy 602 Designations
| D | 2.4633 - NiCr25FeAlY |
| UNS | N06025 |
Alloy 602 Chemical Composition
| Min | Balance | 24 | 8 | 0.15 | - | - | - | 1.8 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | - | - |
| Max | Balance | 26 | 11 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
Alloy 602 Physical Properties
| 7.93 g/cm3 (0.29 lb/in3) at 25℃(77℉) | 1,340 - 1,400 ℃(2,444 - 2,552 ℉) | 1.01 (Maximum) |
| Specific Heat | 447/0.107 | 488/0.117 | 516/0.123 | 583/0.139 | 626/0.150 | 636/0.152 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10.4/72.2 | 14.0/97.1 | 18.4/127.7 | 24.1/167.2 | 28.2/195.7 | 30.6/212.3 |
| Electrical Resistivity | 123 | 126 | 131 | 131 | 132 | - |
| Modulus Of Elasticity | 215/31.2 | 201/29.2 | 189/27.4 | 154/22.3 | 118/17.1 | -/- |
| Co-efficient of Thermal Expansion | -/- | 14.27/7.93 | 14.9/8.28 | 16.0/8.89 | 17.31/9.62 | -/- |
Alloy 602 Mechanical Properties
| Yield Strength MPa/ksi |
270/39.2 | 220/31.9 | 180/26.1 | 170/24.7 |
| Tensile Strength MPa/ksi |
675/97.9 | 625/90.6 | 560/81.2 | 420/60.9 |
| Elongation % |
30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
Welding Alloy 602
When welding nickel alloys and special stainless steels, the following information should be taken into account:
A separately located workplace, which is specifically separated from areas in which C steel is being processed, must be
provided. Maximum cleanliness is required, and drafts should be avoided during gas-shielded welding.
Tools that have been used for other materials may not be used for nickel alloys and stainless steels. Only stainless steel
brushes may be used. Processing and treatment machines such as shears, punches or rollers must be fitted (felt, cardboard, films) so that the workpiece surfaces cannot be damaged by the pressing in of iron particles through such equipment, as this can lead to corrosion.
Welding Filler
| It is recommended to use the same type of welding filler for welding: |
|---|
|