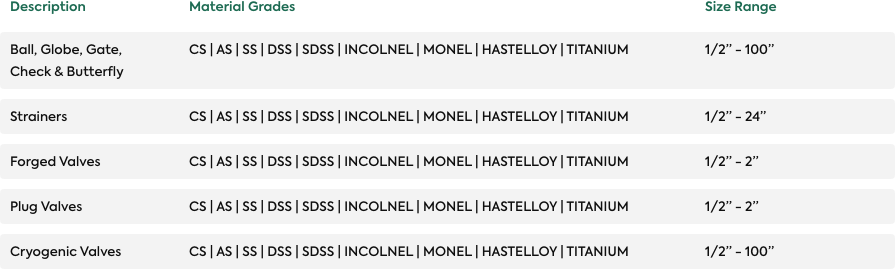
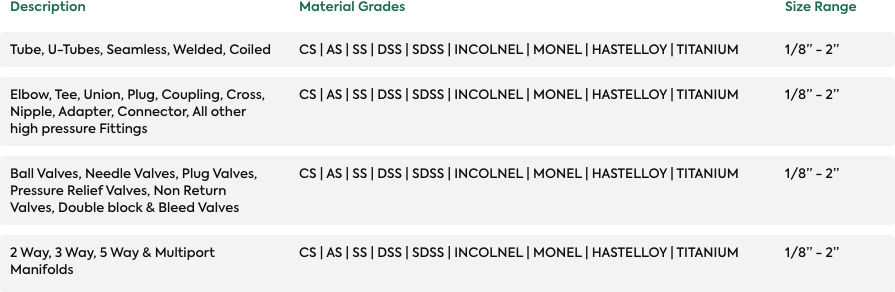
Forms






Nickel 200 and 201 Applications
Unalloyed nickel combines good mechanical properties with good corrosion resistance. In application temperatures above
300°C (572°F), Nickel 201, which stands out for a low C-concentration, is preferable over Nickel 200. The
lowered C-concentration reduces strength and the work hardening rate, and it raises ductility.
Typical applications are:
- Food manufacturing such as handling of cooling brine, fatty acids and fruit juices due to the material’s resistance against acids.
- Alkalis and neutral salt solutions and against organic acids.
- Tanks in which fluorine is produced and where it reacts with hydrocarbon (CFC) due to the material’s resistance against fluorine.
- Storage and transport of phenol.
- Production and treatment of caustic soda.
- Production of synthetic fibres and soaps.
- Production of hydrogen chloride and chlorination of hydrocarbons such as benzene, methane and ethane.
- Production of vinyl chloride monomer due to the material’s resistance against dry chlorine gas and hydrogen chloride in increased temperatures.
- Electrical and electronic components.
- Electrode contacts and current conductors in batteries.
- Current conductors in alkali fuels.
Nickel 200 and Nickel 201 are unalloyed nickel with a nickel concentration of at least 99.2%. Nickel 201 is the low carbon version of Nickel 200.
They are characterized by:
- Excellent resistance in alkaline media.
- High ductility in a wide temperature range.
- Ferromagnetism.
- High electrical and thermal conductivity.
Nickel 201-200 Standards
| Bar | 17752 17740 |
B 160 B564 |
SB 160 SB 564 |
| Sheet | 17740 17750 |
B 162 | SB 162 SA 578 |
| Strip | 17740 | B 162 B 730 |
SB 162 |
| Wire | 17740 | - | - |
Nickel 201-200 Designations
| EN | 2.4066 (200) / 2.4068 LC-Ni 99.2 (201) |
| UNS | N02200 (200) / N02201 (201) |
Nickel 201-200 Chemical Composition
Nickel 200
| Min | - | - | 99.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max | 0.1 | 0.005 | - | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.15 |
Nickel 201
| Min | - | - | 99.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max | 0.01 | 0.005 | - | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.15 |
Nickel 201-200 Physical Properties
| 8.9 g/cm3 bei 20 ℃ (556 lb/ft3) at 68 ℉ | 1,435 - 1,445 ℃(2,610 - 2,630 ℉) | 0.61 T | 360 ℃ (68 ℉) |
| Specific Heat | 456/0.109 | 500/0.119 | 525/0.125 | 565/0.135 | 590/0.141 |
| Electrical Resistivity | 9 | 19 | 37 | 45 | 51 |
| Modulus Of Elasticity | 205/29.7 | 196/28.4 | 175/25.4 | 140/20.3 | -/- |
| Co-efficient of Thermal Expansion | -/- | 13.9/7.72 | 15.2/8.44 | 16.2/9.0 | 16.7/9.28 |
Alloy 201/200 Mechanical Properties
Mechanical Properties of Nickel 200
| Yield Strength MPa/ksi |
100/14.5 |
| Tensile Strength MPa/ksi |
370/53.7 |
| Elongation % |
40 |
Mechanical Properties of Nickel 201
| Yield Strength MPa/ksi |
80/11.6 | 65/9.43 | 55/7.98 | 40/5.8 |
| Tensile Strength MPa/ksi |
340/49.3 | 275/39.9 | 240/34.8 | 150/21.8 |
| Elongation % |
40 | - | - | - |
Welding Alloy 200/201
The use of the following fillers is recommended for gas-shielded welding methods:
| Welding rods and wire electrodes |
|---|
|